Tim Royston-Webb, CEO, SentryBay
Keyloggers discreetly and methodically record each touch and keystroke made by a digital device user, aiming to gather valuable information. Despite being perceived as tools exclusively utilized by the cyber elite, it is astonishing how readily accessible and user-friendly they have become in contemporary times. In this overview, we examine the various types of keyloggers that currently exist, their diverse range of applications (both beneficial and malicious), and the urgent necessity for implementing protective measures.
Keylogger: What It Is and Why It’s Dangerous
A keylogger is a software that captures and stores every keystroke made on a computer. These keyloggers are commonly used as spyware, malware, or antivirus programs. If you have one of these keyloggers installed on your computer, it will record all the information you type, such as usernames, passwords, bank account numbers, credit card details, and even your social media profiles. Worryingly, keyloggers are capable of recording everything you type, even if it is not displayed on the screen.
Hackers may also deploy keyloggers through malware, often using phishing techniques like deceptive emails that trick users into clicking on malicious links to steal personal data including PINs, passwords, and other sensitive information.
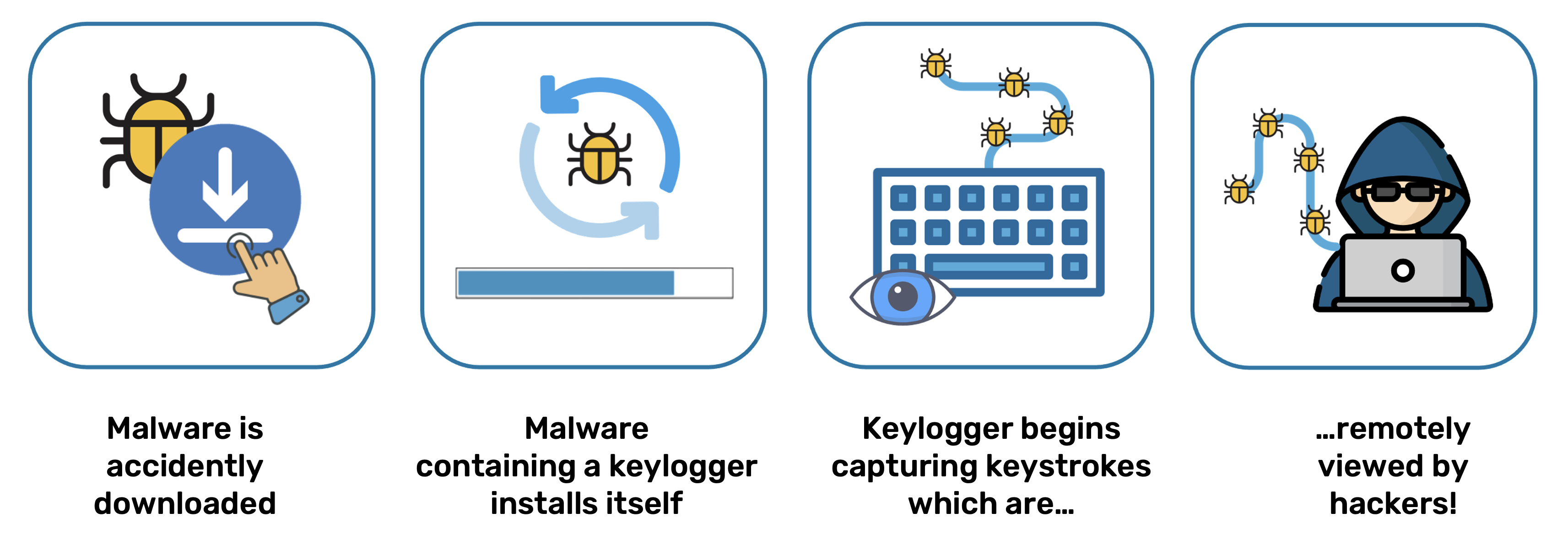
How Keyloggers are Deployed via Malware
Various Types of Keyloggers
There is a wide range of hardware and software devices available today that have the capability to monitor and record computer keyboard input:
- Software-based keyloggers gained popularity in the 1980s. While some were created with malicious intent, others, such as those embedded in Windows 10, aimed to enhance the user experience through improved predictive text abilities. However, the rise of artificial intelligence and voice-activated devices like Amazon’s Alexa has raised concerns. The “always listening” feature of these devices has become a topic of contention.
- USB keyloggers, which can be easily purchased online and disguised as innocent USB drives. Despite their harmless appearance, they are digital Trojan horses. An example of their misuse occurred in 2017 when a university student was expelled for using a hardware keylogger to manipulate academic scores.
- Smartphone-based keyloggers have emerged because of the numerous sensors present in mobile phones. By manipulating motion detection sensors, software can decipher typing habits. Reports have indicated that accuracy levels of up to 97% can be achieved using smartphone data alone.
- Acoustic keyloggers utilize the unique sounds produced by each key on a computer keyboard. By recording and analyzing these sounds, these keyloggers can reconstruct entire documents. Research conducted at the University of California, Berkeley, has shown that over 96% of a document’s content can be reconstructed from keystroke sounds.
- Electromagnetic keyloggers are capable of intercepting and decoding the faint electromagnetic discharges emitted by keyboards. These keyloggers can even penetrate physical barriers with the use of finely calibrated receivers.
Keyloggers Serving Legitimate Purposes
Although the term “keylogger” is often associated with negative connotations, it is important to recognize that many keyloggers serve legitimate and ethical purposes. These include improving software user experiences, enabling parents to monitor their children’s online activities, assisting IT professionals in diagnosing technical issues, and protecting communal tech platforms from misuse. YouTube, with its extensive range of informative content, caters to inquisitive individuals by providing guidance on various subjects, including software creation. Among these resources are tutorials on keyloggers, which are promoted for educational enrichment. While these tutorials can empower and educate genuine learners, they also pose a potential risk by facilitating malicious activities. This dual nature highlights the importance of consuming content discerningly and applying knowledge ethically.
Shielding against Keyloggers with SentryBay
To minimize the risk of falling victim to keyloggers, it is crucial to prioritize knowledge and proactive defence. This can be achieved through various measures such as regularly updating software, implementing robust two-factor authentication, utilizing virtual keyboards, employing cutting-edge anti-keylogger tools, and conducting physical examinations.
Protection against software-based keyloggers, the most elusive kind of keyloggers, is provided by SentryBay’s Armored Client solution. The Armored Client takes a layered approach to protecting endpoint devices being used remotely to access your business applications and data. Whether your employees or contractors are using unmanaged BYOD / BYOPC or managed endpoint devices, all your corporate apps are targeted on the endpoint and run in a secure session.