According to a report by HIPAA Journal, the healthcare industry experienced a significant increase in data breaches in 2023, reaching an unprecedented level. Cybersecurity concerns persistently trouble the industry, leading to this alarming trend. The journal’s analysis of HHS (Department of Health and Human Services) data reveals that over 133 million patient records were compromised in 2023, which is more than double the number recorded in 2022 (51.9 million).
The rise in healthcare data breaches can largely be attributed to phishing, which continues to be a prominent threat. Indeed, the Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG) also reports a significant increase in phishing attacks since 2020. In 2022, a total of 707 health care data breaches impacted approximately 52 million patients, also reported by the HIPAA Journal. This analysis is based on data from the Department of Health and Human Services’ Office for Civil Rights (OCR), which monitors compliance with health care data privacy regulations. According to federal law, health care organizations are obligated to inform individuals when their medical data has been compromised due to a breach.
Phishing attacks serve as a convenient method for cyber threat actors to target their desired victims, and their effectiveness lies in the fact that a small, yet significant proportion of emails manage to entice recipients to click on them. As per the 2022 Verizon Data Breach Investigations (DBIR) Report, the data obtained from phishing simulations reveals that, on average, nearly 3% of phishing emails are clicked.
The most significant health care data breach on record took place in 2015, exposing nearly 80 million Anthem Inc. records. Although the number of incidents among all health plans in 2022 was slightly lower compared to the previous year, there has been a noticeable upward trend in breaches in recent years. These breaches are typically caused by hacking or IT-related incidents.
Primary Objective of Phishing
The primary objective of phishing is to pilfer credentials, enabling threat actors to infiltrate accounts that house sensitive information. Moreover, phishing is employed to gain unauthorized access to email accounts, facilitating business email compromise attacks. According to Verizon’s findings, over 40% of Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks involve the acquisition of credentials through phishing tactics. Additionally, phishing serves to deliver malware and acts as a crucial entry point for initiating ransomware attacks on networks.
Phishing attacks are growing in complexity, and as the number of these cyberattacks continues to rise, it is crucial for security teams to prioritize blocking them. According to a 2021 survey, email phishing is the primary concern for 90% of IT professionals due to the potential damage they can cause and the significant resources required to address these attacks. In the survey, over 50% of IT professionals stated that they spend an equal amount of time dealing with phishing attacks as they do on other cybersecurity issues, while under 40% highlighted that resolving phishing attacks demands the most resources compared to other types of attacks.
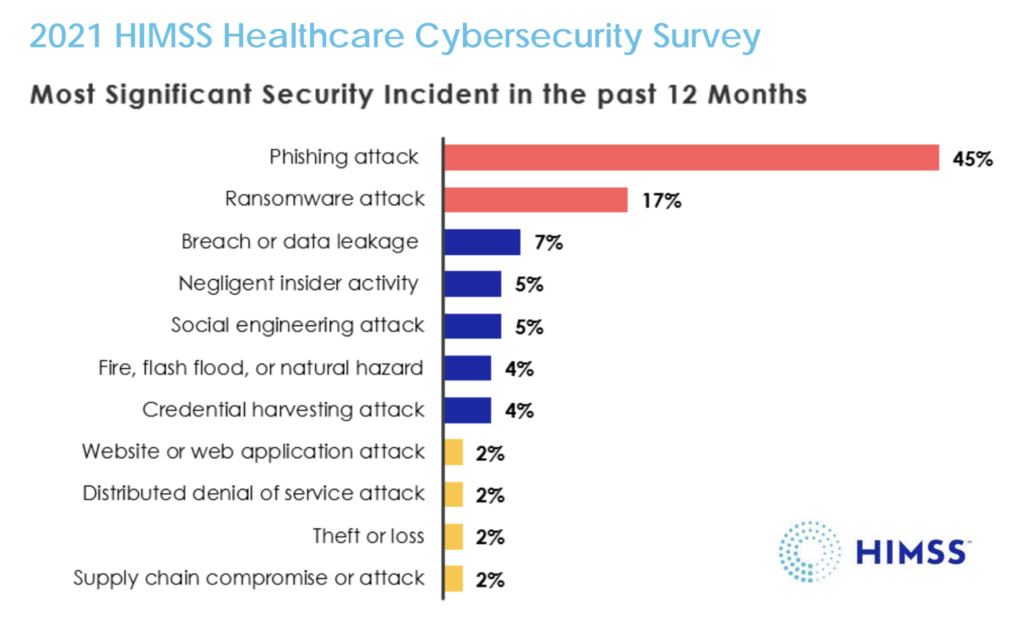
According to the survey, over 80% of the organizations surveyed reported a rise in phishing attacks since the beginning of the pandemic. IBM’s data supports this, revealing that 17% of companies encountered a data breach caused by phishing in 2021.
Financial Consequences for Healthcare Organizations
Phishing attacks can have significant financial consequences for healthcare organizations. A survey conducted by the Ponemon Institute in 2021 revealed that the cost of these attacks has quadrupled over a 6 year period. Currently, the average financial toll of a phishing attack stands at a staggering $15 million per year for companies operating in the United States. This represents a substantial increase from the $4 million recorded in 2015. Additionally, U.S. companies now dedicate a yearly budget of $6 million solely for recovery from BEC attacks. Moreover, these organizations, which have an average workforce of just over 9,000 employees, suffer a loss of 65,000 hours each year due to phishing attacks.
The 2021 Internet Crime Report from the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) reveals that there were over 300,000 complaints filed regarding phishing attacks in 2021. This makes phishing the leading cause of complaints in terms of the number of victims. The reported losses associated with these attacks amounted to just under $45,000,000 in 2021. Additionally, there were nearly 20,000 complaints related to BEC attacks, which often involve phishing. In 2021 alone, BEC attacks resulted in losses of $2,000,000,000. It is worth noting that between June 2016 and December 2021, BEC scams accounted for a staggering $40 billion in losses.
Healthcare Data Phishing
In accordance with the HITECH Act, the HHS commenced the publication of summaries regarding healthcare data breaches consisting of 500 or more records in 2009. Between October 1, 2009, and December 31, 2021, 4,000 breaches involving the protected health information of over 500 individuals have been reported, with the number of breaches steadily increasing each year. Nearly 20% of these breaches, which amounts to more than 800 incidents, are categorized as healthcare phishing attacks or instances where email accounts were hacked. This figure does not encompass the numerous malware and ransomware attacks that originated from phishing emails.
The prevalence of phishing as the primary attack vector in U.S. healthcare cyberattacks cannot be overstated. According to the 2021 HIMSS Healthcare Cybersecurity Survey, 45% of respondents identified phishing attacks as the root cause of their most significant security incidents!
The consequences of phishing attacks are far-reaching, often resulting in data breaches involving hundreds of thousands, and in some cases, millions of compromised records. These breaches occur when employees unwittingly disclose their credentials or unknowingly download malware by falling victim to deceptive phishing emails.
Healthcare Organizations Who Paid the Price
Over the past few years, numerous healthcare organizations have fallen victim to large-scale and costly data breaches. These incidents serve as a stark reminder of the ongoing threat posed by phishing in the healthcare sector:
- Anthem Inc., a healthcare company, disclosed in February 2015 that it had experienced a cyberattack and data breach. This incident marked the largest healthcare data breach ever reported, affecting approximately 78.8 million records of its plan members. The New York Times reported that the attack originated on February 18, 2014, when a user at one of Anthem’s subsidiaries fell victim to a phishing email. As a result, malware was downloaded, granting hackers remote access to computers, and enabling them to navigate through various systems. The attack compromised at least 50 accounts and 90 systems, including Anthem’s data warehouse.
- Iowa Health System (UnityPoint Health) experienced a phishing campaign between March and April 2018. During this time, several employee email accounts were compromised due to phishing emails that appeared to be sent internally from a UnityPoint executive. These compromised accounts contained the protected health information of 1,421,107 patients. The attack was believed to have been conducted to divert payroll and vendor payments. This incident marked the second major phishing attack reported by UnityPoint Health that year, with a previous attack compromising 16,000 records according to Secure Reading.
- Lafourche Medical Group reported that a hacker had accessed an email account with protected health information in March 2021 via a phishing attack, which attempts to trick users into divulging sensitive data or downloading malware. Yahoo Finance reports the health information of 34,862 individuals may have been exposed.
- Los Angeles County Departments of Health and Mental Health faced a ransomware attack in May 2016 reported the Los Angeles Times, followed by a phishing campaign a few months later. This incident emphasizes the critical need for security awareness training among the workforce. Shockingly, 108 employees fell victim to the phishing emails, resulting in compromised email accounts. These accounts held the protected health information of 749,017 individuals.
- Magellan Health Inc., a prominent insurance company listed on the Fortune 500, fell victim to a highly sophisticated social engineering phishing attack in April 2020 as reported by SC Media. The attackers cunningly impersonated one of Magellan Health’s clients, successfully infiltrating their network and deploying ransomware. This breach had a significant impact, affecting not only 1,013,956 Magellan Health members but also other units within the organization. It is estimated that approximately 1.7 million records were compromised because of this attack. It is worth noting that Magellan Health had previously reported a phishing attack in the preceding year, which affected 55,637 plan members.
- Mednax Services, Inc., a Florida-based HIPAA business associate, offers revenue cycle management and administrative services to healthcare organizations. In December 2020, MEDNAX disclosed that a hacker had gained access to multiple email accounts within its Microsoft 365 environment in June 2020. These compromised accounts contained the protected health information of 1,290,670 individuals. MEDNAX was providing support and services to American Anesthesiology, which is owned by North American Partners in Anesthesia. As a result, the records of 1,269,074 American Anesthesiology patients were compromised reports Thomson Reuters.
- Oregon Department of Human Services fell victim to a spear phishing attack in May 2019, where 9 employees were deceived, granting the attackers access to their accounts for a period of 19 days. These compromised email accounts held sensitive personal data of individuals enrolled in welfare and children’s services programs, such as their names, addresses, and Social Security numbers. The breach impacted a staggering 625,000 individuals according to the Statesman Journal.
- Premera Blue Cross, a health insurer announced in 2015 that the records of 10.4 million current and former health plan members had been compromised. The compromised records contained sensitive information such as credit card numbers, Social Security numbers, and more reported Healthcare IT News. The cyberattack began in May 2014 using phishing emails, which facilitated the installation of malware. This malware allowed the hackers to gain access to Premera Blue Cross systems, where they remained undetected for over 9 months.
- Transformative Healthcare notified the HSS regarding a data breach that occurred in April 2023. In the breach notification letters sent on December 27, Transformative Healthcare clarified that the breach was associated with Fallon Ambulance Services, a company it acquired in 2018. The Record states, following the conclusion of the investigation on December 27, the company established that the personal information of approximately 912,000 individuals had been accessed. As a gesture of support, the company is providing the affected individuals with two years of complimentary identity protection services.
Financial Penalties Incurred by Healthcare Organizations
In addition to the expenses associated with remediating phishing attacks, issuing breach notification letters, and paying for identity theft protection services for breach victims, regulators may also impose financial penalties.
HIPAA-regulated entities are required by the HIPAA Security Rule to implement technical, administrative, and physical safeguards to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of electronic protected health information. Failure to implement appropriate safeguards to mitigate the risk of phishing attacks can result in penalties for non-compliance with HIPAA regulations.
For instance, in 2015, the University of Washington Medicine faced a $750,000 financial penalty due to a data breach caused by malware that originated from a phishing attack. The attack involved a fraudulent email with an attachment containing malicious code that downloaded malware.
Another example is the phishing attack on Anthem’s systems, which resulted in a $16 million penalty from the HHS’ Office for Civil Rights (OCR) to address HIPAA violations. Anthem also settled a multi-state action with state attorneys general and paid a penalty of $48.2 million. Similarly, the Premera Blue Cross cyberattack, initiated through a phishing email, led to an OCR penalty of $6.85 million and a $10 million multistate settlement. In December 2023, the OCR also announced it had reached a $480,000 settlement with Lafourche Medical Group over its 2021 data breach. The OCR’s investigation found Lafourche failed to conduct a risk analysis to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities before the attack, and that the medical group didn’t have policies or procedures in place to regularly review its system activity.
SentryBay – Defending Healthcare Providers from Costly Phishing Attacks
In today’s rapidly evolving digital healthcare landscape, the importance of robust cybersecurity measures cannot be overstated. Developing a security program that prioritizes both individuals, including patients and healthcare professionals, and devices can enable medical organizations to effectively regulate access and manage all endpoints to protect healthcare providers from the costly phishing attacks outlined above, while ensuring comprehensive coverage of end-users and connected devices.
“In the past, network security controls used to dominate the security budgets of healthcare providers. However, with the increasing use of endpoint devices, the boundaries of network perimeters have been greatly diminished,” said Brent Agar, Director of Business Development, SentryBay North America. “As a result, medical facilities are now seeking a comprehensive approach to security that covers all entry points to the network. By integrating network and endpoint isolation security, healthcare providers can have a better understanding of the various security threats they face, both in real time and through historical analysis. While network security remains crucial, it is no longer effective to solely rely on physical systems, which are too rigid for today’s dynamic network environment.”
The team at SentryBay are acutely aware of the financial and reputational challenges faced by healthcare organizations due to phishing attacks and have developed our patented DataSAFE product specifically to address them. By leveraging SentryBay’s holistic approach to cybersecurity, healthcare providers can enhance their resilience against phishing attacks, mitigate data breach risks, and safeguard patient confidentiality and trust.